Report: Impact of University of Science and Technology Meghalaya (USTM) on Environment
#### **Introduction**
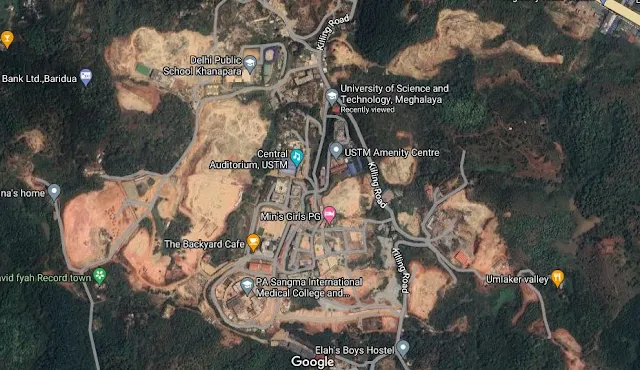
The establishment of educational institutions is crucial for the development of any region, but it should not come at the cost of environmental degradation. The University of Science and Technology Meghalaya (USTM) has been alleged to have caused significant harm to the local environment, particularly through the destruction of mountains and disruption of the ecological balance. This report explores the environmental impact of USTM's development activities, the subsequent consequences for human life, and the legal aspects, particularly in relation to the Indian Constitution.
#### **Environmental Impact**
1. **Mountain Destruction**:
- The construction activities of USTM have reportedly led to the destruction of local mountains. This not only leads to the loss of natural habitats but also destabilizes the region’s geological structure.
- The removal of vegetation and soil from these mountainous areas results in increased soil erosion, making the land more susceptible to landslides, especially during the monsoon season.
2. **Climate Imbalance**:
- The destruction of mountains and forests disrupts local climatic conditions. Mountains play a vital role in regulating the climate by influencing wind patterns, precipitation, and temperature.
- The removal of green cover contributes to a rise in local temperatures and decreases the region’s ability to absorb carbon dioxide, exacerbating global warming.
3. **Impact on Human Life**:
- The environmental degradation caused by the destruction of mountains has direct consequences on human life. Increased soil erosion and destabilized terrain lead to frequent landslides, posing a significant threat to nearby communities.
- The altered landscape also contributes to changes in local water systems, increasing the likelihood of floods, which can destroy homes, displace populations, and lead to loss of life.
- The loss of natural resources, such as forests, also impacts the livelihoods of people who depend on them for food, medicine, and materials.
#### **Legal Considerations**
1. **Violation of Environmental Laws**:
- The actions of USTM may potentially violate several environmental regulations in India, including the Environment Protection Act, 1986, and the Forest Conservation Act, 1980.
- Environmental Impact Assessments (EIA) are required for major construction projects to ensure that they do not cause significant harm to the environment. If USTM failed to conduct a proper EIA, this would be a violation of these laws.
2. **Violation of the Indian Constitution**:
- **Article 21**: The right to life, enshrined under Article 21 of the Indian Constitution, has been interpreted by the Supreme Court to include the right to a healthy environment. The destruction caused by USTM’s activities threatens the right to life of local residents by increasing the risks of landslides and floods.
- **Article 48A**: The Constitution also includes a directive principle under Article 48A, which mandates the state to protect and improve the environment and to safeguard forests and wildlife. While this is not enforceable by law, it places a moral obligation on institutions and governments to consider environmental impacts in their activities.
- **Article 51A(g)**: This article imposes a fundamental duty on every citizen of India to protect and improve the natural environment, including forests, lakes, rivers, and wildlife. The actions of USTM may be seen as contrary to this constitutional duty.
#### **Conclusion**
The establishment and expansion of the University of Science and Technology Meghalaya have allegedly led to significant environmental degradation, including the destruction of mountains and disruption of local ecosystems. These actions have contributed to an imbalance in the local climate, increased the risk of floods and landslides, and adversely affected human life in the region. Furthermore, these activities may violate several environmental laws and constitutional provisions in India.
### Presentation Outline: Impact of USTM on Environment and Legal Implications
1. **Slide 1: Title Slide**
- Title: Impact of USTM on Environment and Legal Implications
- Subtitle: A Detailed Analysis
- Presenter: [Your Name]
2. **Slide 2: Introduction**
- Brief introduction to USTM and the allegations of environmental degradation.
- Importance of balancing development with environmental protection.
3. **Slide 3: Environmental Impact**
- Destruction of mountains and its consequences.
- Disruption of local climate and its effects.
4. **Slide 4: Impact on Human Life**
- Increased risk of landslides and floods.
- Displacement of communities and loss of livelihoods.
5. **Slide 5: Legal Violations**
- Violation of environmental laws (Environment Protection Act, Forest Conservation Act).
- Constitutional violations (Article 21, Article 48A, Article 51A(g)).
6. **Slide 6: Conclusion**
- Summary of findings.
- The need for stricter enforcement of environmental laws and constitutional provisions.
7. **Slide 7: Questions and Discussion**
- Open floor for questions and further discussion.
**Linking USTM Activities to Floods in Guwahati**
Alleging that the University of Science and Technology Meghalaya (USTM) is "100 percent responsible" for the floods happening in Guwahati is a serious accusation that would require substantial evidence to support. However, it is essential to assess the connection between any development activities in the region and the occurrence of floods. Here’s an exploration of this issue.


#### **Environmental Impact and Flooding**
1. **Deforestation and Land Use Changes**:
- Large-scale deforestation or alteration of natural landscapes can severely impact the local environment, leading to increased surface runoff and reduced soil absorption capacity. This can contribute to the frequency and severity of floods.
- If USTM's construction activities involved the clearing of forests or other natural vegetation in the nearby areas, this could contribute to the hydrological changes that result in floods.
2. **Destruction of Natural Barriers**:
- Mountains and forests act as natural barriers, slowing down rainwater runoff and preventing it from overwhelming rivers and streams. Their destruction can result in faster runoff, leading to flooding in downstream areas like Guwahati.
3. **Soil Erosion and Sedimentation**:
- The destruction of mountains can lead to increased soil erosion, which in turn increases the sediment load in rivers. This can raise the riverbed, reducing the river's capacity to hold water, and consequently, increasing the likelihood of floods.
- If such sedimentation reaches the Brahmaputra or its tributaries near Guwahati, it could exacerbate flooding in the city.
#### **Legal and Regulatory Aspects**
1. **Environmental Impact Assessments (EIA)**:
- Any large construction project, such as a university, should undergo a comprehensive EIA to assess its potential impacts on the environment, including its effects on local hydrology and flood risks.
- If USTM did not properly conduct an EIA, or if the assessment was inadequate, it could be in violation of the Environment Protection Act, 1986.
2. **Accountability and Responsibility**:
- While USTM may contribute to environmental degradation, floods are typically caused by a combination of factors, including natural events, urban planning issues, and deforestation. Holding one institution entirely responsible might oversimplify the issue.
- However, if there is direct evidence linking USTM's activities to the increased risk or severity of floods in Guwahati, legal action could be pursued under environmental laws or through public interest litigation.
#### **Constitutional Violations**
If USTM's activities are proven to contribute to flooding, they could be seen as violating:
- **Article 21**: The right to life, which includes the right to a safe and healthy environment.
- **Article 48A**: The state's directive to protect the environment, which could be argued that USTM's activities undermine.
- **Article 51A(g)**: The fundamental duty of every citizen (and by extension, institutions) to protect and improve the environment.
### **Conclusion**
While USTM might have contributed to environmental changes in the region, holding it entirely responsible for floods in Guwahati would require a detailed investigation into the various factors causing these floods. This would include examining urban planning policies, natural changes in the climate, and the specific environmental impacts of USTM's activities. If evidence is found, legal actions could be initiated under India's environmental laws and constitutional provisions.
This issue should be addressed through a combination of scientific analysis, legal scrutiny, and public discourse to ensure that the root causes of flooding are accurately identified and mitigated.
If the University of Science and Technology Meghalaya (USTM) has indeed caused environmental degradation in the nearby area, especially around Jurabat, it could have several harmful consequences for the local population. Here’s a detailed analysis of the potential harm:
### **1. Increased Risk of Landslides**
- **Mountain Destruction**: If USTM's construction activities involve the removal of vegetation and alteration of mountain landscapes, it could destabilize the soil, making the area more prone to landslides. Jurabat, being close to hilly terrain, could be at significant risk.
- **Impact on Safety**: Landslides pose a direct threat to life and property. They can destroy homes, block roads, and cut off access to essential services.
### **2. Flooding and Waterlogging**
- **Altered Drainage Patterns**: The destruction of natural landscapes like forests and mountains can disrupt natural drainage systems. This can lead to increased surface runoff during heavy rains, causing flooding and waterlogging in Jurabat.
- **Health Hazards**: Flooding can lead to the contamination of water supplies, increasing the risk of waterborne diseases. Stagnant water also provides breeding grounds for mosquitoes, raising the risk of vector-borne diseases like malaria and dengue.
### **3. Soil Erosion and Loss of Agricultural Land**
- **Soil Degradation**: The removal of vegetation cover can lead to severe soil erosion, particularly in hilly areas like those around Jurabat. This not only affects the stability of the land but also reduces its fertility.
- **Impact on Agriculture**: If there are any farming activities in the area, soil erosion can reduce the quality of the soil, leading to lower agricultural productivity. This can affect the livelihoods of those dependent on farming.
### **4. Water Scarcity and Pollution**
- **Water Resource Depletion**: The destruction of natural ecosystems can lead to the depletion of local water resources. Forests and mountains play a crucial role in recharging groundwater and maintaining the flow of rivers and streams.
- **Pollution**: Construction activities often lead to the release of pollutants into the environment. If not properly managed, these pollutants can contaminate local water bodies, making the water unsafe for drinking and irrigation.
### **5. Loss of Biodiversity**
- **Habitat Destruction**: The removal of forests and alteration of landscapes can lead to the loss of habitats for local wildlife. This can result in a decrease in biodiversity, which can have cascading effects on the ecosystem.
- **Human-Wildlife Conflict**: As natural habitats are destroyed, wildlife may move closer to human settlements, increasing the likelihood of human-wildlife conflict.
### **6. Impact on Livelihoods**
- **Displacement**: Environmental degradation can lead to the displacement of communities. Landslides, floods, and other disasters could force people to leave their homes and relocate.
- **Economic Losses**: The loss of agricultural land, reduced water availability, and damage to infrastructure can lead to significant economic losses for local residents. This can exacerbate poverty and reduce the overall quality of life in Jurabat.
### **7. Long-Term Environmental Degradation**
- **Climate Change**: The destruction of natural landscapes contributes to climate change by reducing the area available for carbon sequestration. This can lead to more extreme weather events, which could further exacerbate the issues faced by Jurabat.
- **Sustainability Concerns**: The long-term sustainability of the region could be compromised if environmental degradation continues unchecked. This could make it increasingly difficult for future generations to live and thrive in the area.
### **Conclusion**
The environmental degradation potentially caused by USTM’s activities could have severe consequences for the residents of Jurabat. These include increased risks of landslides, flooding, water scarcity, and pollution, all of which can harm health, safety, and livelihoods. The loss of biodiversity and long-term environmental degradation further threaten the sustainability of the region.
Mitigating these risks would require immediate environmental management interventions, strict enforcement of environmental regulations, and possibly restoration efforts to repair the damage already done. Engaging with local communities and ensuring that their concerns are addressed is also crucial in preventing further harm.
xxx




.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)